Headlice and Headlice Treatment
New school term – New bugs?
Headlice infestation? Headlice treatments! Urgh…….not again!
New school uniform ripped on day 1? Tick.
New shoes scuffed on day 3? Tick.
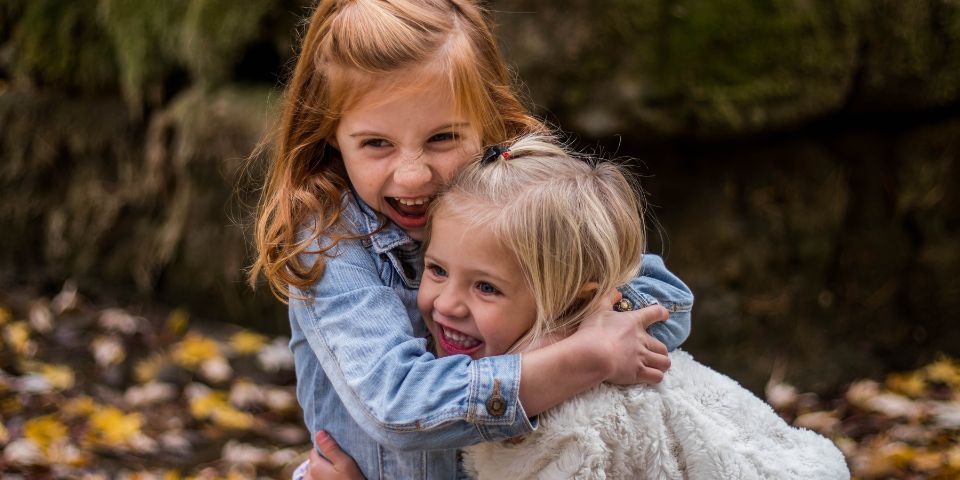
Back to school can be stressful for all sorts of reasons but head lice shouldn’t be one of them!
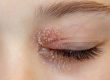
Head lice are a parasitic infection of the scalp caused by Pediculus Humanus Capitis. These parasites live in the hair, close to the scalp so they can bite and feed on the host (human). The biting can cause the scalp to become itchy as well as the lice crawling around on the scalp. The areas can appear to be red espcially at the nape of the neck and behind the ears.
Headlice cannot fly, so are spread by head-to-head contact often when children are playing or hugging. It is a good idea to check children’s scalps weekly as detailed below. If live lice are found then checking the whole family’s scalps is a great idea.
Some facts about Headlice:
- Headlice can’t jump or fly
- They like long or short hair, as long as it’s clean!
- Head lice can’t live off the body for more than 24hrs
- Head lice can spread by head-to-head contact.
Natural headlice treatment measures you can try;
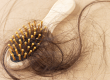
- Apply Aloe vera gel, lavender oil and tea tree oil mixed together topically to coat the scalp and hair. Put on a shower cap to protect your pillow and go to bed. Wash your hair as normal in the morning. Comb hair in small sections with a metal nit comb (Pictured), to remove dead headlice.
2. The key is regular and consistent checking of the hair and scalp – weekly is best and using a metal comb is easier.
Plastic combs often break. Children often scratch at the nape of the neck and behind the ears.

3. Neem oil or coconut oil applied to the hair and scalp will make the metal comb glide easily through the hair. It also makes it harder for the lice to cling on to the hair shaft.
Hopefully your children will not bring home any ‘new friends’ in their scalps! If they do, feel free to call me as there are lots of homeopathic remedies to treat and prevent head lice infestations.